







































Babylon Makes BTC a Yield-Bearing Asset Without Custodians
 BABY
BABY GEN
GEN READ
READ SECURITY
SECURITY ATOM
ATOM| Key Points: - Babylon enables native BTC staking with no wrapping, custody, or bridges required. - EOTS and timestamping ensure trustless slashing and fast unbonding. - Genesis Chain coordinates staking across PoS chains using Bitcoin-secured infrastructure. |

Babylon allows users to stake Bitcoin directly from the Bitcoin chain, locking BTC into native contracts without using wrapped assets, custodians, or bridges. Validators are coordinated via the Babylon Genesis Chain, a Cosmos SDK Layer 1, which handles finality signatures, timestamp aggregation, and staker-matching across PoS chains.
With security innovations like Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS), Bitcoin-based timestamping, and finality gadgets, Babylon enables trustless slashing, fast unbonding, and Byzantine-resilient cross-chain staking.
Unlike traditional models that fragment liquidity and rely on centralized signers, Babylon offers a decentralized, self-custodial solution for yield generation on Bitcoin, positioning BTC as a foundational security asset in the multi-chain staking economy.
How Babylon Bitcoin Staking Works
Babylon introduces a system where Bitcoin can be staked directly on its native chain, eliminating the need for asset wrapping, bridging, or third-party custody. The protocol enables Bitcoin holders to lock BTC into a native contract, providing economic security for external Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chains.
Rewards are issued by the PoS chains benefiting from this security, while the BTC itself remains secured on the Bitcoin network. Unbonding is available at any time, subject to a withdrawal delay (e.g., 3 days), and slashing mechanisms ensure penalties for misbehavior.
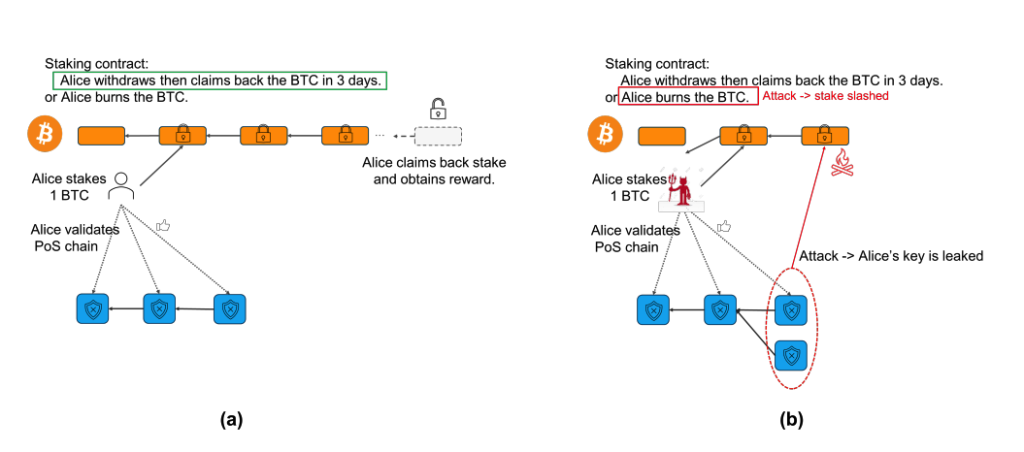
If a validator violates consensus safety, a portion of their BTC can be burned, enforcing compliance through cryptographic accountability.
Key Security Innovations (Finality Gadgets, EOTS, Timestamping)
Three core cryptographic components support Babylon’s staking framework:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS) | Ensures that double-signing leads to key exposure, enabling the network to slash misbehaving stakers by destroying locked BTC. Provides trustless and automated slashing without smart contracts. |
| Finality Gadgets | Introduces an additional finality round that operates alongside PoS consensus. Validators sign finalized blocks using EOTS. Conflicting finality signatures constitute a verifiable safety breach, triggering slashing procedures. |
| Bitcoin Timestamping | Leverages the Bitcoin chain to timestamp PoS blocks, mitigating long-range attacks and enabling faster unbonding. Unlike typical PoS chains reliant on social consensus for finality, BabyIon uses verifiable timestamps for precision and speed. |
These innovations allow Babylon to deliver a modular, trust-minimized staking system that is compatible with Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) PoS protocols across chains.
Role of the Babylon Genesis Chain
The Babylon staking architecture is coordinated via the Babylon Genesis Chain, a Cosmos SDK-based Layer 1. While BTC remains on the Bitcoin chain, the Genesis Chain provides the control infrastructure to manage cross-chain operations.
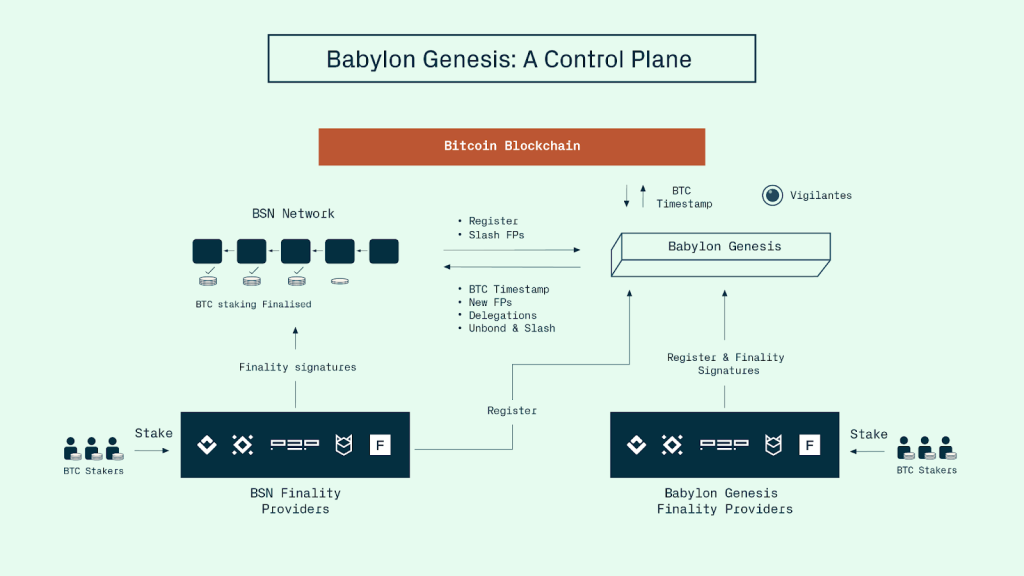
Key functions of the Genesis Chain include:
- Validator coordination and tracking
- Timestamp aggregation from the Bitcoin network
- Finality signature verification
- Staker-to-chain matching
Launched in early 2023 on testnet, the Genesis Chain has connected with over 30 Cosmos SDK-based blockchains, establishing itself as the intermediary layer for Bitcoin-secured PoS staking.
Traditional Staking vs. Babylon Staking Model
Traditional methods like wrapped BTC (e.g., wBTC, sBTC) involve locking BTC in custodial systems or smart contracts and issuing mirrored assets on PoS chains, which carry several risks. In contrast, Babylon eliminates these concerns.
| Aspect | Traditional Staking (e.g., wBTC, sBTC) | Babylon Staking Model |
|---|---|---|
| Custodial Dependencies | Involves locking BTC in custodial systems or smart contracts | Eliminates custodial dependencies with full self-custody of BTC |
| Smart Contract Vulnerabilities | Risks from vulnerabilities in smart contracts | No reliance on smart contracts, ensuring greater security |
| Centralized Signer Control | Control over assets by centralized signers | No centralized control, fully decentralized |
| Liquidity Fragmentation | Liquidity is fragmented across different wrapped assets | Interoperable with multiple PoS ecosystems, ensuring unified liquidity |
| Slashing Logic | Dependent on smart contract and external validators | Transparent and trustless slashing logic built into the native model |
| Third-Party Bridges | Requires third-party bridges for asset transfers | No reliance on third-party bridges, native PoS staking mechanism |
By staking directly from the Bitcoin chain, Babylon establishes BTC as a trust-minimized, yield-generating security asset, extending its utility while maintaining its foundational integrity.
| DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is provided as general market commentary and does not constitute investment advice. We encourage you to do your own research before investing. |

