






































North Korean IT Personnel Target Blockchain Firms Globally
 SOL
SOL
 UTED
UTED
 IDTT
IDTT
 SUSHI
SUSHI
 READ
READ
- Main event, North Korean IT infiltration of blockchain abroad, impacts projects and security.
- It increases cybersecurity risks globally.
- Identity fraud facilitates operational network expansion.
North Korean IT operatives have reportedly expanded their infiltration activities to blockchain companies outside the United States, targeting firms in the UK through identity fraud. Google’s latest Threat Analysis Group report indicates a broadening scope due to increased U.S. regulatory scrutiny.
The increased infiltration poses cybersecurity concerns for blockchain companies globally, with potential for espionage, data breaches, and revenue losses. Enhanced identity verification and security measures are crucial to mitigating these risks.
North Korea Targets UK Amid Global Cybersecurity Concerns
A broader infiltration scope is evident as North Korean IT personnel expand efforts to infiltrate blockchain projects in Europe, particularly in the UK. This follows tightened U.S. regulatory measures, prompting these activities.
Companies face heightened risks of data breaches, corporate espionage, and revenue diversion to North Korea, consistent with past incidents involving significant financial losses. The need for enhanced security protocols is more pronounced than ever.
"They’ve established a global ecosystem of fraudulent personas to enhance operational agility. This suggests the rapid formation of a global infrastructure and support network." — Jamie Collier, Lead Threat Intelligence Advisor, Google’s Threat Analysis Group (GTIG)
Sophisticated Infiltration Tactics Highlight Need for Robust Defenses
Did you know? North Korean cyber infiltration of the blockchain sector is not new. In 2021, SushiSwap fell victim to a $3 million hack, highlighting ongoing vulnerabilities in decentralized finance.
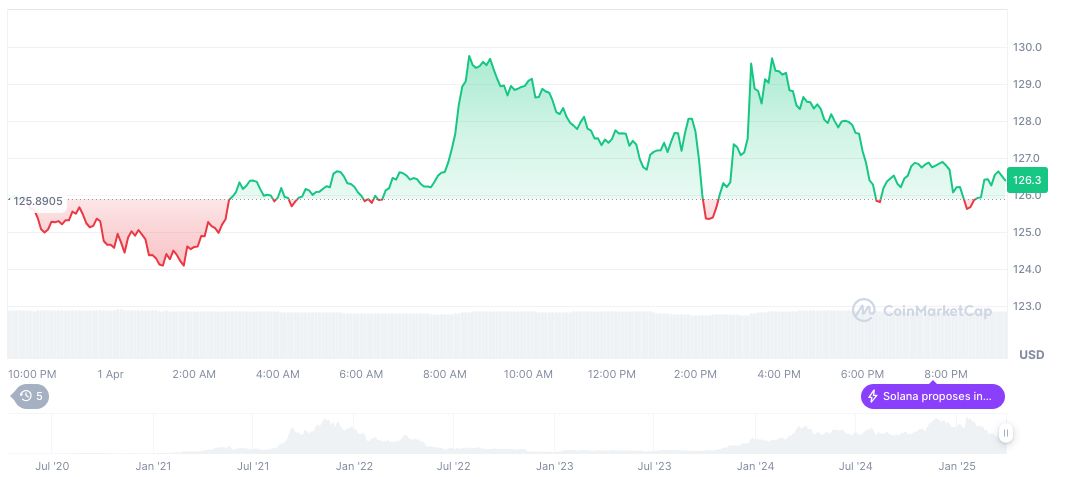
As detailed by CoinMarketCap, Solana (SOL) is currently priced at $125.99, with a notable 7-day decline of 12.25%. Its market capitalization stands at $64.57 billion, comprising 2.37% of the cryptocurrency market.
Coincu analysts emphasize the potential necessity for regulatory bodies to enhance monitoring frameworks and for firms to reinforce cybersecurity protocols, given North Korea's growing sophistication in using technology for infiltration.
Read original article on coincu.com
